HackInParis 2019 training
Attacking and securing BLE and NFC/RFID devices based on smart locks and access control systems

During this training we will focus on two technologies implemented very commonly in various IoT devices, including among others smart locks and access control systems : BLE and NFC/RFID.
Bluetooth Low Energy (Smart, 4) is one of the most popular and rapidly growing IoT technologies. Unfortunatelly the prevalence of technology does not come with security, and the knowledge on how to comprehensively assess such devices seems very uncommon. This training aims to address this need. Multiple hands-on exercises with dedicated individual devices (included in takeaway hardware set) guarantee to thoroughly understand from both developer’s and pentester’s perspective how BLE works and how can be attacked. We will perform: wireless sniffing, spoofing, cloning, replay, Denial of Service, Man in the Middle, authentication and command-injection attacks. Practical exercises will include opening multiple real “smart” locks, investigating proprietary protocols, demystifying and breaking “military grade encryption” and abusing excessive services.
NFC/RFID on the other hand, has been around us for quite long. However, the vulnerabilities pointed out years ago, probably won’t be resolved in a near future. It is still surprisingly easy to clone most access control cards used for buildings today. Among other practical exercises performed on real installations, the attendees will reverse an example, quite popular hotel access system, and as a result will be able to open all the doors in facility.
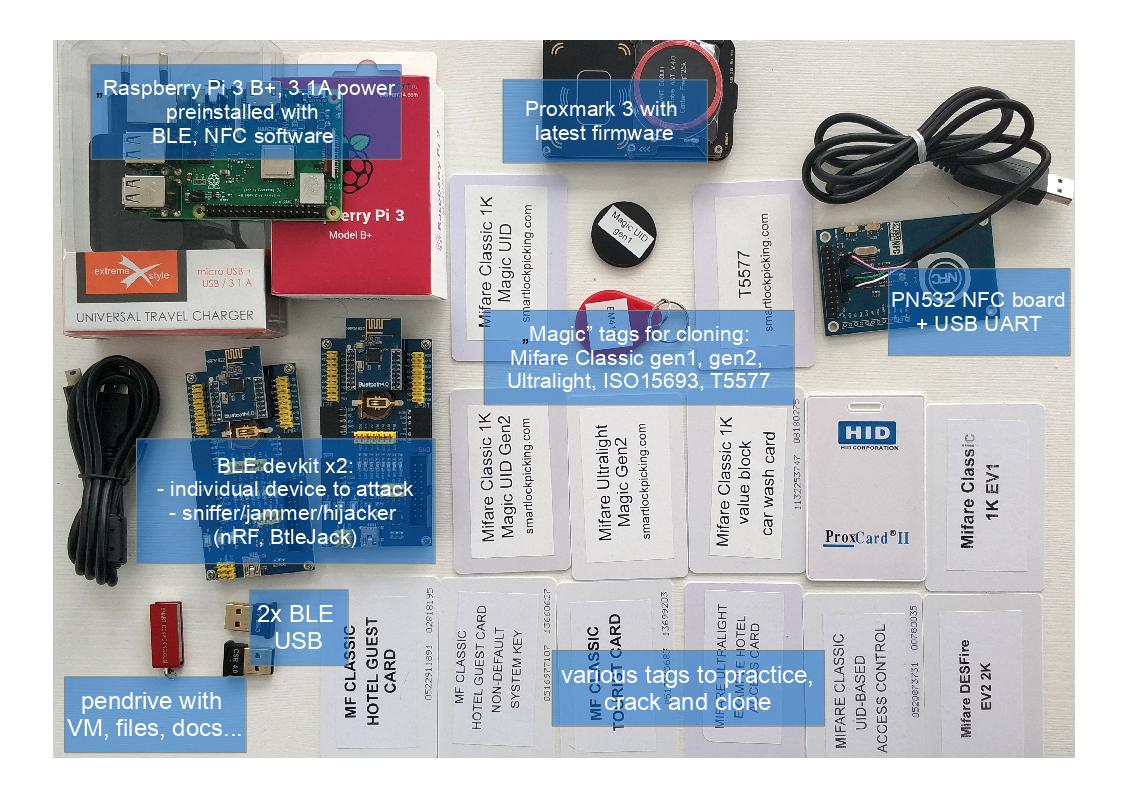
The training includes a hardware pack (over 150 EUR value) for each student, consisting among others of preconfigured Raspberry Pi, Proxmark3, “magic” tags, NFC board, dedicated Bluetooth device to attack and BLE sniffer. The hardware will allow you to crack and clone NFC/RFID tags, sniff and analyse Bluetooth Low Energy connections and practice most of the exercises later at home.
Pre-requisites
- At least basic familiarity with Linux command-line, Kali, Wireshark.
- Scripting/programming skills will be very helpful.
Target audience
- Pentesters, security professionals
- IoT developers
- Anyone interested
Material to bring by attendees
- Laptop capable of running Kali Linux in VM and USB port.
- Android smartphone with BLE and NFC support will be very helpful.
- You can bring your own BLE device or NFC card to verify its security.
Course syllabus
1. NFC
UID-based access control - practical exercises on example reader + door lock
- UID lengths, formats
- clone Mifare UID using “Chinese magic” card and provided hardware
- how to emulate contactless cards and unlock UID-based system using just a smartphone (Android, iOS), without any additional hardware
- how to clone a card by making its picture - decoding numbers printed on cards
- emulate card using Proxmark, Chameleon Mini
- brute-force - is it possible in practice to guess other cards UID?
- countermeasures against attacks
Wiegand - wired access control transmission standard
- sniff the data transmitted from access control reader using Raspberry Pi GPIO
- decode card UID from sniffed bytes, clone the card
- replay card data on the wire to open lock
- available Wiegand sniffers/repeaters
Mifare Classic & its weaknesses - practical exercises based on hotel door lock system, ski lift card, bus ticket and others
- Mifare Classic - data structure, access control, keys, encryption
- default & leaked keys
- reading & cloning card data using just a mobile phone
- cracking keys - nested, darkside attacks
- libnfc tools - mfoc, mfcuk, MiLazyCracker
- cracking Mifare using provided hardware
Reverse-engineering data stored on card
- decoding access control data (room number, date) stored on card by an example hotel system
- creating hotel „emergency card” to open all the hotel doors unconditionally
Mifare Ultralight
- data structure
- reading, cloning, emulating
- example data stored on hotel access card
Introduction to Proxmark, Low Frequency cards (EM4100, HID Prox).
Summary of known attacks and security issues of Mifare Plus, DESFire, Ultralight C, HID iClass, Hitag …
2. Bluetooth Smart (Low Energy)
based on multiple devices (including 7 various smart locks) and tools developed by the trainer: GATTacker BLE MITM proxy and deliberately vulnerable Hackmelock (consisting of Android mobile application and lock device simulated on Raspberry Pi).
Theory introduction
- What is Bluetooth Smart/Low Energy/4.0, how it is different from previous Bluetooth versions?
- Usage scenarios, prevalence in IoT devices
- Protocol basics
- Advertisements, connections
- Central vs peripheral device
- GATT - services, characteristics, descriptors, handles
- Security features - pairing/encryption, whitelisting, MAC randomization
- Security in practice: own crypto in application layer
- Hardware required for BLE assessment
BLE advertisements and beacons
- iBeacon, Eddystone, Physical Web
- Simulating beacons - using mobile phone, Linux scripts, other devices.
- How to get free beer by abusing beacon-based reward application
- scanning for visible devices, hcitool, bleah, GATTacker, …
- decoding data in advertisements
- advertisement spoofing - Denial of Service, device impersonation
Sniffing BLE connections using RF layer hardware
- Ubertooth, nRF sniffer, other hardware
- Wireshark filters, tips&tricks
- sniffing static cleartext password of a smart lock and other devices using provided hardware
HCI dump (Linux, Android) - setup, analysis, difference from RF-layer sniffing, replay/fuzzing possibilities.
Attacking services exposed by devices
- mapping device services and characteristics
- interacting with devices that do not require pairing/authentication
- example unlocked AT command interface via BLE service of a smart lock
Device spoofing, active MITM interception
- how to perform “man in the middle” attack on BLE connections
- available tools: GATTacker, BtleJuice.
- MAC address cloning
- analysing intercepted traffic
- Denial of Service attacks
Replay attacks
- intercept transmission
- analyse authentication protocol weakness in example smart lock
- perform replay using tools or a mobile phone, and unlock the device
Mobile application analysis, attacks on proprietary authentication and protocols
- decompile Android app, locate relevant source code fragments
- understand proprietary BLE communication protocol - commands, data exchanged with device
- based on example smart lock, discover protocol weakness, create exploit to open the lock without knowing current password or prior sniffing
- exploit the vulnerability using just a mobile phone - nRF Connect macros
- verify other vendor’s claims on “Latest PKI technology” and “military grade encryption”
Relay attacks - abusing automatic proximity features (e.g. smart lock autounlock).
Remote access share functions and their weaknesses - how to bypass timing restrictions.
How to create own, independent server-side API for device - based on a real smart lock vendor, which disappeared and shut the servers, effectively rendering the device e-waste.
Introduction to Web Bluetooth, Bluetooth Mesh, Bluetooth 5.0
BLE Hackmelock - open-source software emulated device with multiple challenges to practice at home.
BLE best practices and security checklist - for security professionals, pentesters, vendors and developers.
Each student will receive:
- course materials in PDFs (several hundred pages)
- all required additional files: source code, documentation, installation binaries, virtual machine images on a pendrive
- Hardware pack for hands-on exercises consisting of:
- Bluetooth Smart hardware sniffer and development kit based on nrf51822 module
- 2 Bluetooth Low Energy USB dongles
- Raspberry Pi 3 (+microSD card and 3.1A power adapter), with assessment tools and Hackmelock installed for further practice at home.
- Proxmark 3 with latest firmware
- NFC NXP PN532 board (libnfc)
- Multiple NFC/RFID tags, including “magic UID”, T5577, Ultralight, EV1, …
Register
Register here:
Share this post
Twitter
Google+
Facebook
Reddit
LinkedIn
StumbleUpon
Email